OVERVIEW
Symptoms of diabetes developing during pregnancy are classified under gestational diabetes. Like other types of diabetes, gestational diabetes affects how your cells use sugar (glucose) — your body’s main fuel. Gestational diabetes causes high blood sugar that can affect your pregnancy and your baby’s health.
Complications from pregnancy can be alarming, but there’s good news. Expectant moms can help control gestational diabetes by eating healthy foods, exercising and, if necessary, using medication. Taking good care of yourself can ensure a healthy pregnancy for you and a healthy start for your baby.
Blood sugar usually returns to normal soon after delivery in gestational diabetes. But if you’ve had gestational diabetes, you’re at risk for future type 2 diabetes. You’ll continue working with your health care team to monitor and manage your blood sugar.
Causes
Patients aged over 85 who have had cataract surgery seem to be at a greater risk of this condition. It is however rare among others who have had a cataract surgery affecting only 0.1% cases of cataract surgery. Cases of Endophthalmitis after a blood infection are even rarer. Around 2 to 15% of all endophthalmitis cases are caused due to infections borne in blood.
Endophthalmitis Can Occur :
Patients aged over 85 who have had cataract surgery seem to be at a greater risk of this condition. It is however rare among others who have had a cataract surgery affecting only 0.1% cases of cataract surgery. Cases of Endophthalmitis after a blood infection are even rarer. Around 2 to 15% of all endophthalmitis cases are caused due to infections borne in blood.
Risk factors of Endophthalmitis :
Symptoms
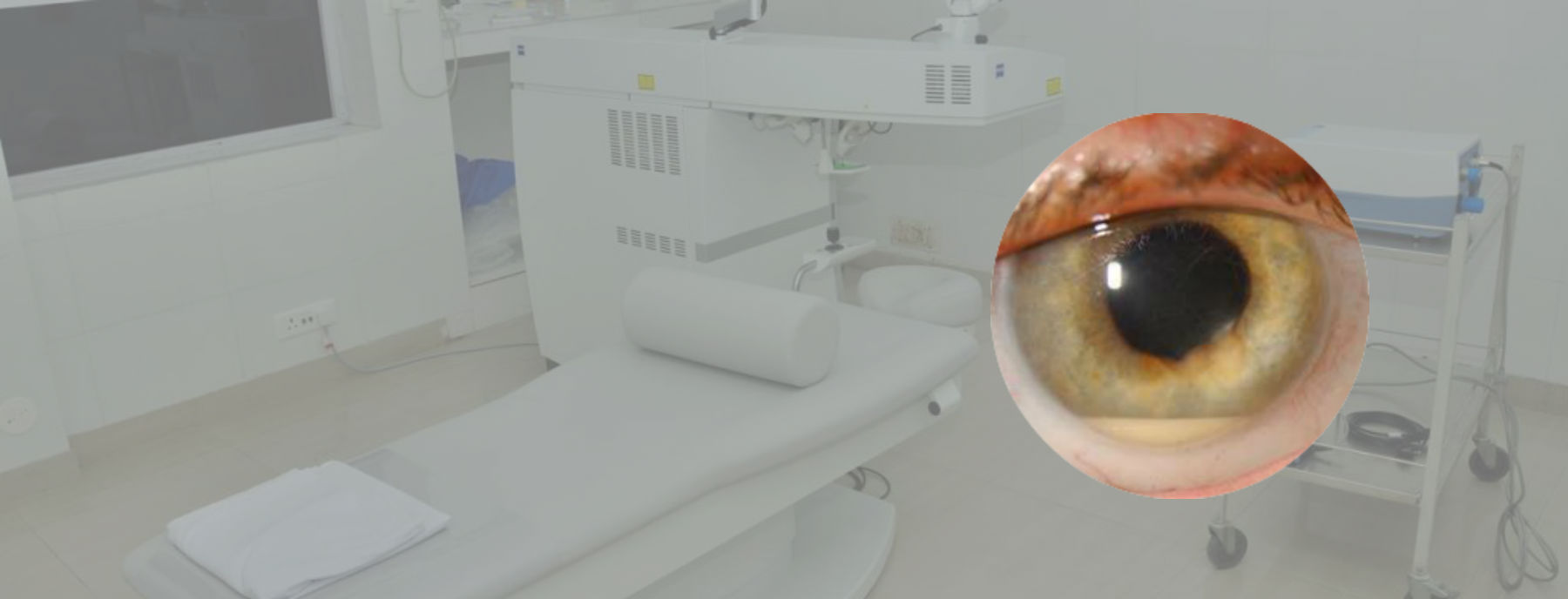
- One of the most common features includes a red and inflamed eye.
- There is blurring or decreasing vision
- There is pain in the eye. Endophthalmitis may also be present without pain.
- The patient usually provides a history of ocular surgery or trauma. Endophthalmitis after a surgery may present with sudden decrease of vision and increasing eye pain one to several days after surgery. Some cases may appear after a week to a month (or more) after surgery.
- The patient may have a condition that has diminished his or her immunity.
- The eye lid may appear swollen and the eye may appear red in acute cases while in long term or chronic cases there is gradual decrease of vision and gradually increasing redness and minimal or no pain.
- Those patients who have a generalized infection leading to Endophthalmitis may have other features like fever, acute illness etc.
Diagnosis
A detailed history and examination of the eye is undertaken for diagnosis. The eye appears swollen and the conjunctiva appears red and suffused. The physician may also note presence of a pus spot in the anterior chamber of the eye. This is viewed by a slit lamp. Slit-lamp examination also shows severe inflammation in the anterior chamber and the vitreous especially in early post operative Endophthalmitis.
Fungal Endophthalmitis is caused by fungi like Candida. These may be present in patients with AIDS or those after an eye injury. The patient complains of presence of floaters or moving objects in vision, pain in both eyes. On examination using an ophthalmoscope there are presence of fluffy yellow-white retina lesions that appear as cotton balls with or without bleeding points over the retina.
Endophthalmitis caused due to microbial keratitis shows damage to the cornea. These are usually associated with contact lens wear especially with extended wear and poor hygiene. There may also be tear film deficiency or long term use of steroid drops in the eyes.
Diagnosis thus includes examination with –
Complication
Possible complication includes loss of vision. There may be chronic pain as well. In most cases however treatment may lead to a good response. To prevent Endophthalmitis after an operation, adequate care and treatment of pre-existing infections as well as maintenance of operative hygiene is important.
Treatment
Hospital admission is usually necessary for patients with Endophthalmitis. Delay or lack of adequate treatment may lead to loss of vision. After an eye injury a tetanus immunization is given to prevent tetanus. Treatment is usually targeted towards the cause of the condition –