OVERVIEW
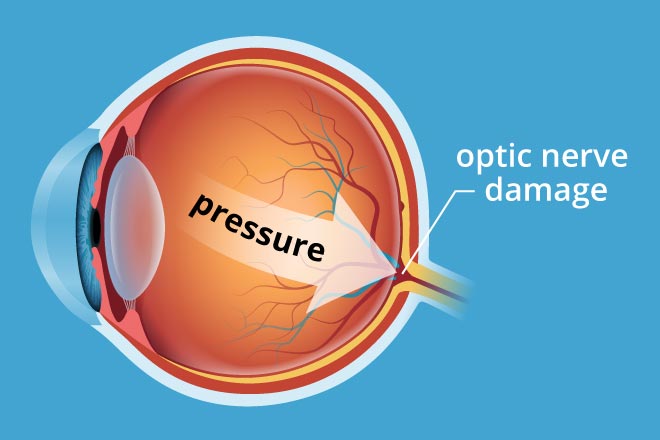
Glaucoma is a serious and rare condition of the eye where the optic nerve is damaged resulting in loss of side or peripheral vision, tunnel vision and blindness. In a normal eye, there is a small anterior chamber filled with clear fluid called aqueous humor. This fluid flows out of an open angle (drainage angle) between the iris (colored portion of eye ball) and the cornea. At the open angle the fluid flows out of the eye through a spongy network. If there is a reduction in the flow of fluid at this position, it raises the pressure in the eye called intraocular pressure (IOP), damages the optic nerve and causes glaucoma. Glaucoma can affect both eyes.
Optic nerve is a bundle of nerve fibers that carries signals from the retina of the eye to the brain which are processed as images. Damage to the optic nerve cannot be reversed. Hence, there is no cure for glaucoma as the lost vision cannot be restored. However, early diagnosis and detection can preserve your vision and prevent vision loss.
Types of Glaucoma
Primary Open-angle glaucoma : This happens when the meshwork at the drainage angle is unable to drain the aqueous humor effectively. There are no symptoms to begin with except blank or black spots in the vision. However, by the time blank spots become evident in day-to-day activities, there has been considerable damage to the optic nerve. The damage to optic nerve occurs at different IOPs for different individuals. Your ophthalmologist or eye specialist will determine your target IOP and help your maintain it. Often raised IOPs are missed at the first eye pressure testing. However, routine eye pressure testing by trained ophthalmologist can often diagnose this early.
Normal-tension glaucoma : The normal eye pressure is about 21 mm Hg. However, some people suffer an optic damage at 21 mm Hg or pressures below 21 mm Hg. This is called normal tension glaucoma. This is treated just like open angle glaucoma and occurs because for these individuals the target IOP is low. It presents with blind spots in the field of vision.
Closed-angle glaucoma (Angle-closure glaucoma or Narrow-angle glaucoma) : This happens when the iris blocks the flow of aqueous humor. The IOP rises very fast. Individuals with farsightedness (hyperopia) or those of Asian descent are at higher risk for developing this type of glaucoma.
Causes
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms differ with the type of glaucoma. However, there are no signs and symptoms in early stages of glaucoma. Thereafter, a person may develop black spots in vision, loss of peripheral vision, colored halos, see rainbow colors, have headaches, and develop tunnel vision or blindness.
Diagnosis
Since glaucoma does not present with early signs and symptoms, it is detected through a detailed eye examination that includes the following tests:
- Visual acuity test : Your Doctor will ask you to read a chart at different distances to assess how clearly you can see the alphabets.
- Visual field test measures : Your doctor will use a special instrument called perimeter to check your peripheral or side vision. Only one eye is checked at a time and the other eye is covered with a black patch. In a sitting position you will be asked to focus straight ahead at a target. A computer will generate noises and send out flashes of light in every direction. Some noises are not accompanied by a flash of light. You will be asked to press a button when you see a flash of light. Your doctor may perform this test every six to twelve months to monitor the change.
- Dilated eye exam or Ophthalmoscopy : Your doctor will put some eye drops into your eyes and ask you to wait for some time with your eyes closed. This will help dilate your pupils. One eye is tested at a time. Your eye specialist will use a special magnifying glass (ophthalmoscope) to look into your eyes to examine the retina and the optic nerve. In glaucoma the nerve fibers of the optic nerve are damaged and cause cupping of the optic nerve. This cupping of the optic nerve causes blank spots in your vision. After the eye examination your near vision may remain blurred for some hours so you will not be able to drive back home.
- Tonometry : Your doctor will use a special instrument (tonometer) to measure the IOP. Your doctor will put some eye drops to numb the white of your eyes. One eye is tested at a time. The instrument will then be placed on the white of the eye to take the eye pressure. Normal IOP varies between 10 and 21 mm Hg, and is generally around 21mmHg for most eyes.
- Pachymetry : Your doctor will put some eye drops to numb your eyes. One eye is tested at a time. A special instrument is then used to measure the thickness of your cornea. Your eye care professional uses an ultrasonic wave instrument to measure the thickness of your cornea.
- Gonioscopy : Your doctor will use a mirrored lens inspect the drainage angle of your eye. One eye is tested at a time. If the drainage angle is not working well then it is an open-angle glaucoma; if the angle is partially closed it is closed-angle glaucoma; if the iris completely blocks the angle it is a dangerous variety of closed angle glaucoma.
Treatment
Glaucoma can be treated with medicines and surgery.
- Glaucoma medication : Your doctor will prescribe eye drops to lower your eye pressure. The drops either slow down the formation of aqueous humor or improve its drainage at the drainage angle. You will need to use the eye drops daily, in dose prescribed by the doctor.
- You will also have to tell your doctor about all the medications and supplements you are taking as some drugs cause glaucoma.
- Glaucoma surgery: Your doctor will perform different types of surgeries to improve the drainage of aqueous humor. The different surgeries are:
- Laser trabeculoplasty : Usually this is used to treat open-angle glaucoma. There are two types of laser trabeculoplasties: ALT or argon laser trabeculoplasty and SLT or selective laser trabeculoplasty. In ALT surgery, your doctor will use laser to make tiny burns at regular intervals in the trabecular meshwork at the drainage angle. This improves the drainage function of the meshwork. In SLT, the laser burns specific cells in the meshwork to lower the IOP. In SLT the laser is of lower energy and applied in shorter spurts than in ALT. Almost half the patients undergoing a trabeculoplasty, develop increased eye pressure within five years. Repeat trabeculoplasty can be performed in some while most use eye drops to keep the eye pressure low.
- Laser iridotomy : This surgery is recommended for closed angle glaucoma where the drainage angle has become very narrow. Your doctor will use laser to make a small hole in the upper part of iris to improve the flow of aqueous humor.
- Peripheral iridectomy : If laser iridotomy is unable to treat the closed angle glaucoma or where it is unlikely to benefit, your doctor may perform a peripheral iridectomy. Your doctor will improve a small piece of iris to improve the flow of aqueous humor. Since most closed angle glaucoma can be treated with medications or laser iridotomy, peripheral iridectomy is less commonly performed surgery.
- Trabeculectomy : Your doctor will make a small flap in the white coat of your eye (sclera). A new drainage channel is made for the aqueous humor by creating a filtration reservoir under the conjunctiva (membrane covering the white of the eye). The reservoir looks like a small bump on the eye, but is usually covered by the upper eyelid. The aqueous humor now drains out of the flap made in sclera and collect in the reservoir.